[Spring Cloud MSA] Spring Cloud를 통한 MSA 개발(3) - API Gateway Service
API Gateway Service란?
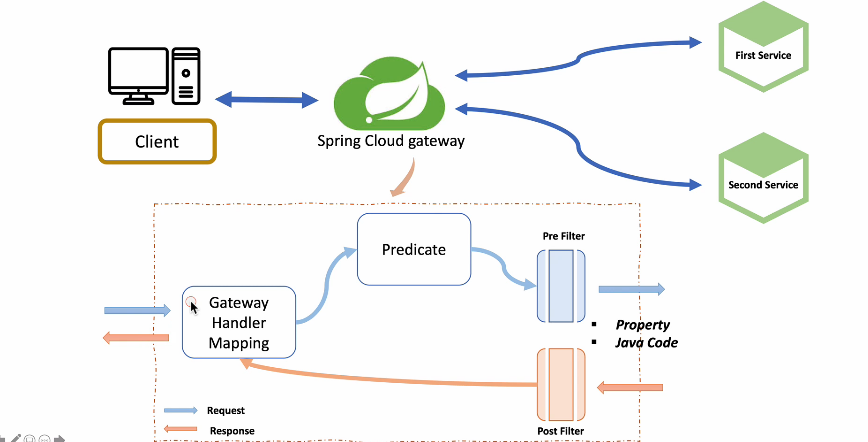
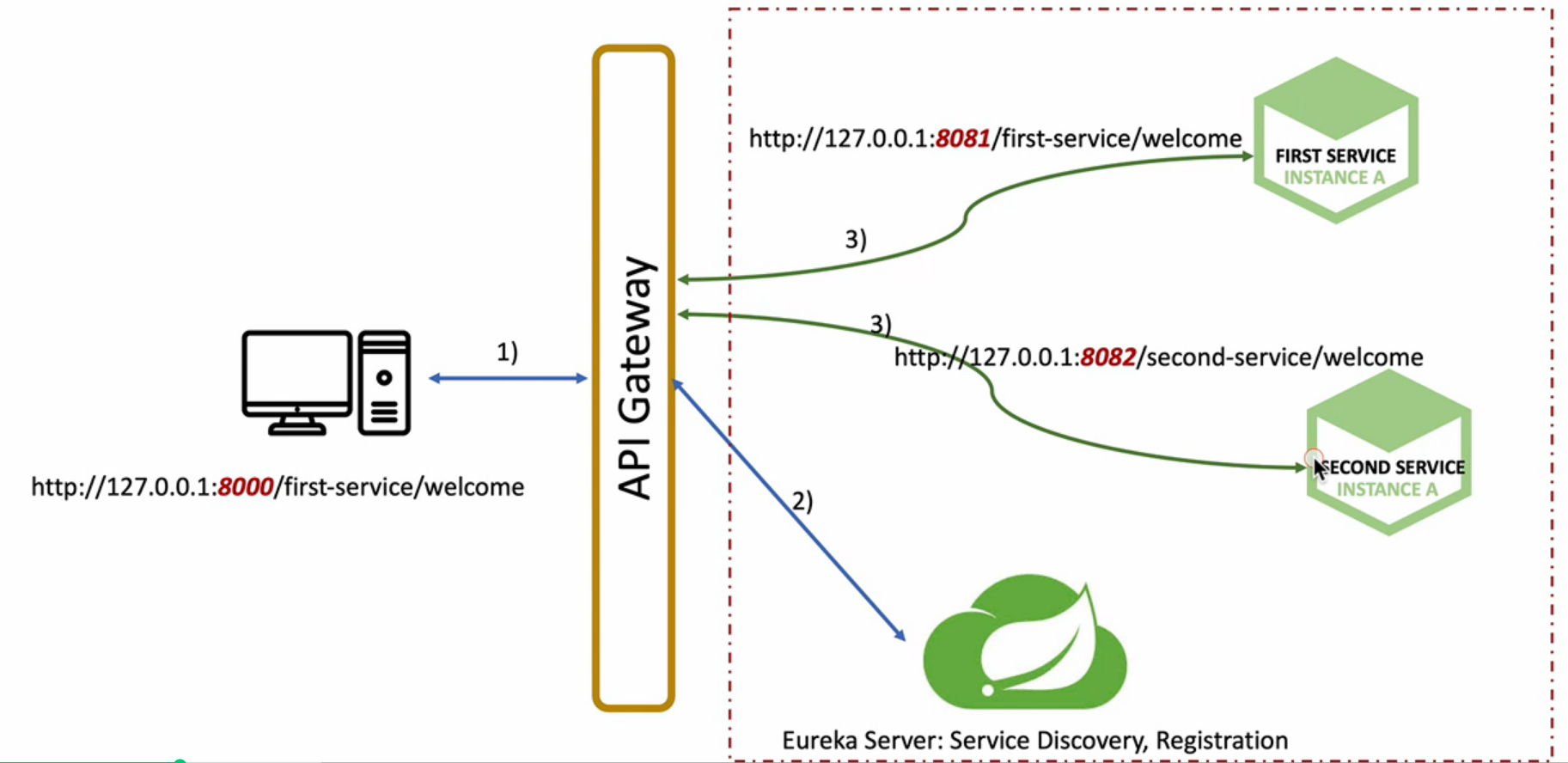
API Gateway Service는 사용자가 설정한 라우팅 설정에 따라서 각 엔드포인트로 클라이언트 대신 요청을 보내고 응답을 받으면 클라이언트에게 전해주는 일종의 프록시 역할을 한다. 시스템의 내부 구조는 숨기고 외부의 요청에 대해서 적절한 형태로 가공해서 응답할 수 있는 장점이 있다.
API Gateway Service를 사용하게 되면 다음과 같은 기능을 이용할 수 있다.
- 인증 및 권한 부여
- 서비스 통합 검색
- 응답 캐싱
- 정책, 회로 차단
- 속도 제한
- 부하 분산
- 로깅, 추적, 상관 관계
- 헤더, 쿼리 문자열 및 청구 변환
- IP 허용 목록에 추가
Spring Cloud Gateway
스프링 클라우드 게이트웨이 서비스를 이용해 API gateway 서비스와 라우팅 서비스를 구현해보자.
간단하게 first-service 와 second-service 두 서비스를 만들어서 스프링 클라우드 게이트웨이를 적용해보자
스프링 부트 프로젝트 생성 - first-service, second-service
Dependencies
- Spring Boot DevTools
- Eureka Discovery Client
- Gateway
FirstServiceController
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/first-service")
public class FirstServiceController {
@GetMapping("/welcome")
public String welcome(){
return "Welcome to First Service";
}
}
SecondServiceController
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/second-service")
public class SecondServiceController {
@GetMapping("/welcome")
public String welcome(){
return "Welcome to Second Service";
}
}
First-Service applcation.yml
server:
port: 8081
spring:
application:
name: my-first-service
eureka:
client:
fetch-registry: false
register-with-eureka: false
Second-Service applcation.yml
server:
port: 8082
spring:
application:
name: my-first-service
eureka:
client:
fetch-registry: false
register-with-eureka: false
이제 게이트웨이 서비스 프로젝트를 생성하자
Dependencies
- lombok
- Gateway
- Eureka Discovery Client
application.yml
server:
port: 8000
eureka:
client:
register-with-eureka: false
fetch-registry: false
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka
spring:
application:
name: apigateway-service
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: first-service
uri: http://localhost:8081/
predicates:
- Path=/first-service/**
- id: second-service
uri: http://localhost:8082/
predicates:
- Path=/second-service/**
gateway.routes 에서 여러 라우트 객체를 등록할 수 있다. first service 와 second service의 라우트 정보를 등록하자. predicates 는 조건절이라고 생각하면 된다. 사용자의 Path 정보가 조건과 같으면 무조건 지정된 uri 로 이동한다.
이제 만든 서비스들의 서버를 실행시키고 localhost:8000/first-service/welcome 으로 들어가보면 요청정보가 그대로 8081포트로 가서 welcome 컨트롤러가 정상작동하는것을 확인할 수 있다.
필터 적용
게이트웨이 라우터를 자바코드에서 필터적용을 해보자.
@Configuration
public class FilterConfig {
@Bean
public RouteLocator gatewayRoutes(RouteLocatorBuilder builder) {
return builder.routes()
.route(r->r.path("/first-service/**")
.filters(f->f.addRequestHeader("first-request","first-request-header")
.addResponseHeader("first-response","first-response-header"))
.uri("http://localhost:8081"))
.route(r->r.path("/second-service/**")
.filters(f->f.addRequestHeader("second-request","second-request-header")
.addResponseHeader("second-response","second-response-header"))
.uri("http://localhost:8082"))
.build();
}
}
자바코드에서 한 필터를 application.yml 에서 적용해보자
spring:
application:
name: apigateway-service
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: first-service
uri: http://localhost:8081/
predicates:
- Path=/first-service/**
filters:
- AddRequestHeader=first-request, first-request-header2
- AddResponseHeader=first-response, first-response-header2
- id: second-service
uri: http://localhost:8082/
predicates:
- Path=/second-service/**
filters:
- AddRequestHeader=second-request, second-request-header2
- AddResponseHeader=second-response, second-response-header2
같은 필터지만 자바코드로 할지 application.yml 에서 할지 정할 수 있다.
Custom Filter
@Component
@Slf4j
public class CustomFilter extends AbstractGatewayFilterFactory<CustomFilter.Config> {
public CustomFilter(){
super(Config.class);
}
@Override
public GatewayFilter apply(Config config) {
//Custom Pre Filter
return (exchange, chain) ->{
ServerHttpRequest request = exchange.getRequest();
ServerHttpResponse response = exchange.getResponse();
log.info("Custom PRE filter: request id -> {}", request.getId());
//Custom Post Filter
return chain.filter(exchange).then(Mono.fromRunnable(()->{
log.info("Custom POST filter: response code -> {}", response.getStatusCode());
}));
};
}
public static class Config {
// Put the configuration properties
}
}
ServerHttpRequest,ServerHttpResponse : Gateway 서버는 톰캣(동기식) 서버가 아니라 Netty(비동기) 서버가 실행되어서 httpServletRequest가 아니다.
application.yml
spring:
application:
name: apigateway-service
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: first-service
uri: http://localhost:8081/
predicates:
- Path=/first-service/**
filters:
- CustomFilter
# - AddRequestHeader=first-request, first-request-header2
# - AddResponseHeader=first-response, first-response-header2
- id: second-service
uri: http://localhost:8082/
predicates:
- Path=/second-service/**
filters:
- CustomFilter
# - AddRequestHeader=second-request, second-request-header2
# - AddResponseHeader=second-response, second-response-header2
first service 와 second service에 각각 Custom filter를 적용시켰다.
Global Filter
@Component
@Slf4j
public class GlobalFilter extends AbstractGatewayFilterFactory<GlobalFilter.Config> {
public GlobalFilter(){
super(Config.class);
}
@Override
public GatewayFilter apply(Config config) {
//Custom Pre Filter
return (exchange, chain) ->{
ServerHttpRequest request = exchange.getRequest();
ServerHttpResponse response = exchange.getResponse();
log.info("Global filter baseMessage: {}", config.getBaseMessage());
if (config.isPostLogger()) {
log.info("Global filter Start: request id -> {}", request.getId());
}
//Custom Post Filter
return chain.filter(exchange).then(Mono.fromRunnable(()->{
if (config.isPostLogger()) {
log.info("Global filter End: response code -> {}", response.getStatusCode());
}
}));
};
}
@Data
public static class Config {
private String baseMessage;
private boolean preLogger;
private boolean postLogger;
}
}
application.yml
spring:
application:
name: apigateway-service
cloud:
gateway:
default-filters:
- name: GlobalFilter
args:
baseMessage: Spring Cloud Gateway Global Filter
preLogger: true
postLogger: true
routes:
- id: first-service
uri: http://localhost:8081/
predicates:
- Path=/first-service/**
filters:
- CustomFilter
# - AddRequestHeader=first-request, first-request-header2
# - AddResponseHeader=first-response, first-response-header2
- id: second-service
uri: http://localhost:8082/
predicates:
- Path=/second-service/**
filters:
- CustomFilter
# - AddRequestHeader=second-request, second-request-header2
# - AddResponseHeader=second-response, second-response-header2
cloud: gateway: default-filters:
- name: GlobalFilter args: baseMessage: Spring Cloud Gateway Global Filter preLogger: true postLogger: true
에서 args는 만든 Global Filter 의 Config 값 설정이다.
localhost:8000/first-service/welcome 에 GET 요청을 보내보자
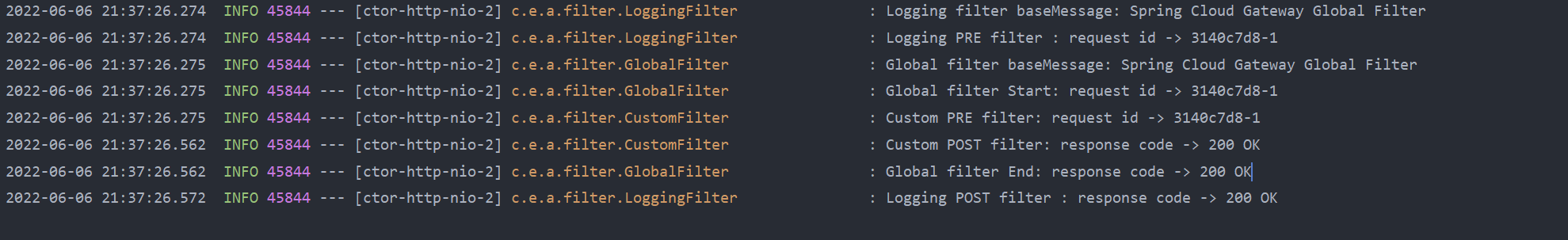
글로벌 필터와 커스텀 필터가 잘 적용된 것을 확인할 수 있다.
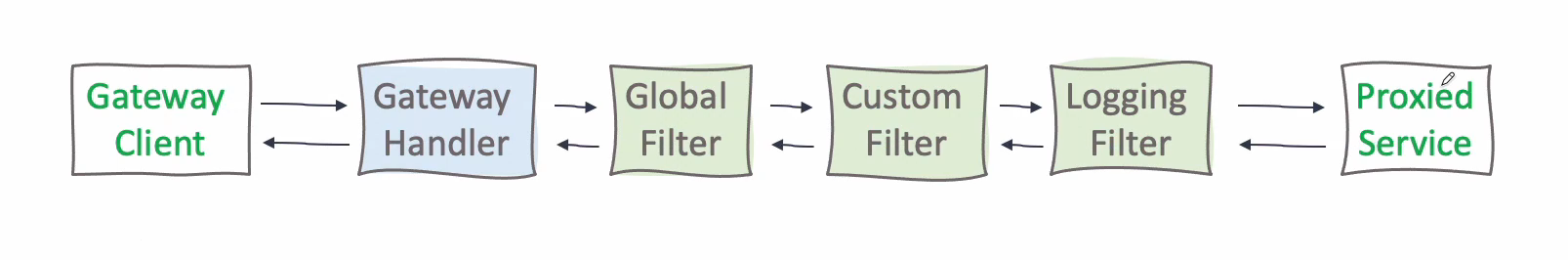
Custom Filter (Logging)
Logging 필터를 만들고 위와 같은 구조로 필터를 적용해보자
@Component
@Slf4j
public class LoggingFilter extends AbstractGatewayFilterFactory<LoggingFilter.Config> {
public LoggingFilter(){
super(Config.class);
}
@Override
public GatewayFilter apply(Config config) {
GatewayFilter filter =new OrderedGatewayFilter((exchange, chain) -> {
ServerHttpRequest request = exchange.getRequest();
ServerHttpResponse response = exchange.getResponse();
log.info("Logging filter baseMessage: {}", config.getBaseMessage());
if (config.isPostLogger()) {
log.info("Logging PRE filter : request id -> {}", request.getId());
}
//Custom Post Filter
return chain.filter(exchange).then(Mono.fromRunnable(()->{
if (config.isPostLogger()) {
log.info("Logging POST filter : response code -> {}", response.getStatusCode());
}
}));
}, Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE);
return filter;
}
@Data
public static class Config {
private String baseMessage;
private boolean preLogger;
private boolean postLogger;
}
}
Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE 로 우선순위를 가장 높게 했다. 이 우선순위를 변경하여 어떤 필터가 먼저 적용될지 정할 수 있다.
application.yml
spring:
application:
name: apigateway-service
cloud:
gateway:
default-filters:
- name: GlobalFilter
args:
baseMessage: Spring Cloud Gateway Global Filter
preLogger: true
postLogger: true
routes:
- id: first-service
uri: http://localhost:8081/
predicates:
- Path=/first-service/**
filters:
- CustomFilter
# - AddRequestHeader=first-request, first-request-header2
# - AddResponseHeader=first-response, first-response-header2
- id: second-service
uri: http://localhost:8082/
predicates:
- Path=/second-service/**
filters:
- name: CustomFilter
# - AddRequestHeader=second-request, second-request-header2
# - AddResponseHeader=second-response, second-response-header2
- name: LoggingFilter
args:
baseMessage: Spring Cloud Gateway Global Filter
preLogger: true
postLogger: true
second-service에만 LoggingFilter을 적용하였다. 참고로 커스텀 필터에 args를 적용하고 싶을 때는 name:CustomFilter 같이 name을 정하고 args를 적어야 한다.
정상적으로 적용이 된것을 확인할 수 있다.
Eureka 연동
유레카 서버에 스프링 클라우드 게이트웨이를 등록하고 first-service 와 second-service 도 등록해보자.
apigateway, first-service, second-service의 application.yml 파일에 유레카 클라이언트 정보를 입력해주자
eureka:
client:
register-with-eureka: true
fetch-registry: true
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka
apigateway 의 application.yml 파일은 추가로 수정해주자
cloud:
gateway:
default-filters:
- name: GlobalFilter
args:
baseMessage: Spring Cloud Gateway Global Filter
preLogger: true
postLogger: true
routes:
- id: first-service
uri: lb://MY-FIRST-SERVICE
predicates:
- Path=/first-service/**
filters:
- CustomFilter
# - AddRequestHeader=first-request, first-request-header2
# - AddResponseHeader=first-response, first-response-header2
- id: second-service
uri: lb://MY-FIRST-SERVICE
predicates:
- Path=/second-service/**
filters:
- name: CustomFilter
# - AddRequestHeader=second-request, second-request-header2
# - AddResponseHeader=second-response, second-response-header2
- name: LoggingFilter
args:
baseMessage: Spring Cloud Gateway Global Filter
preLogger: true
postLogger: true
routes의 uri 부분을 수정해 주었다. 기존엔 localhost:8081 처럼 했지만 이제 디스커버리 서비스에 등록된 마이크로서비스 중에서 해당 마이크로서비스로 포워딩 시킬것이다.
lb://MY-FIRST-SERVICE 는 사용자가 해당 path로 서비스를 요청하면 유레카 서버에 등록된 MY-FIRST-SERVICE를 찾아서 그쪽으로 포워딩 시켜준다.
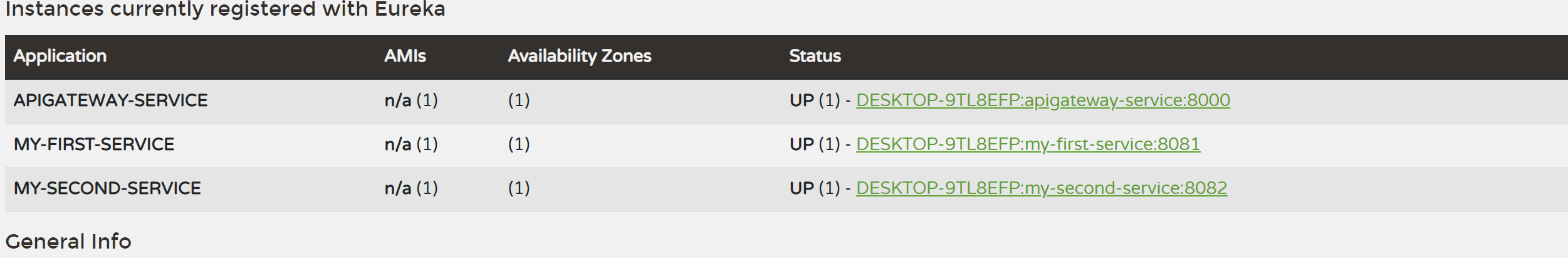
모든 설정을 하고 유레카 서버를 기동시키고 정상적으로 등록이 됬는지 확인해보자.
정상적으로 3가지가 등록된 것을 확인할 수 있다.
localhost:8000/first-service/welcome localhost:8000/second-service/welcome
두 서비스 다 정상적으로 작동하는것도 확인할 수 있다.
로드밸런싱
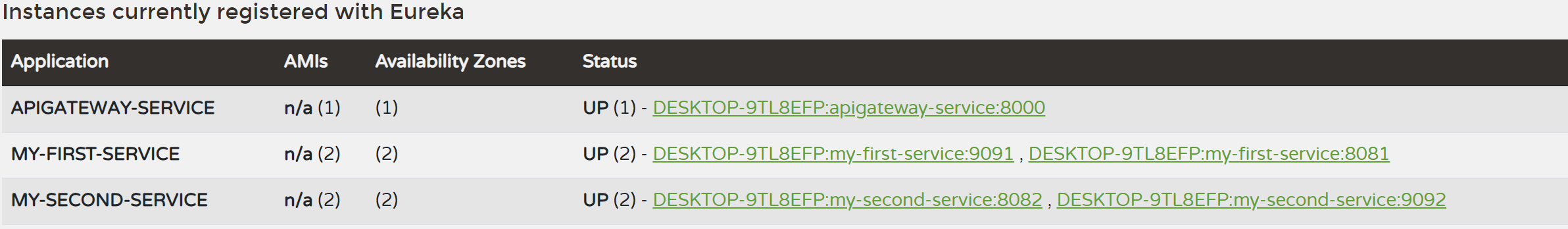
first-service 와 second-service를 하나씩 더 기동시켜 보자. 각각 포트는 9091,9092로 하였다.
유레카 서버에 first-service, second-service 가 2가지 인스턴스가 만들어진것을 확인할 수 있다.
하지만 이렇게 하면 서비스 요청 시 어떤 인스턴스에 요청했는지 알 수가 없다.
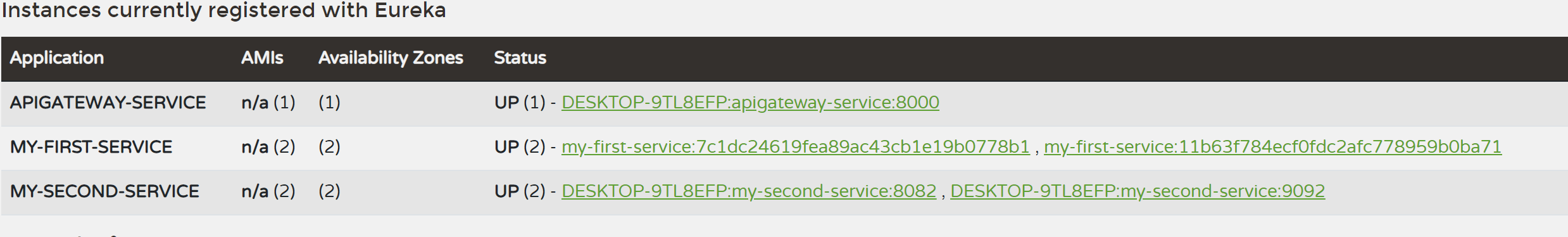
서비스들의 application.yml 파일의 포트번호를 0으로 해서 랜덤포트 번호를 부여하고 인스턴스 아이디를 지정해주자
server:
port: 0
spring:
application:
name: my-first-service
eureka:
client:
register-with-eureka: true
fetch-registry: true
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka
instance:
instance-id: ${spring.application.name}:${spring.application.instance_id:${random.value}}
이제 몇번 포트 서비스가 불려졌는지 알기 컨트롤러에서 포트번호를 출력해보자.
여기선 Environment 객체를 이용할 것이다.
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/first-service")
@Slf4j
public class FirstServiceController {
Environment env;
@Autowired
public FirstServiceController(Environment env){
this.env=env;
}
@GetMapping("/welcome")
public String welcome(){
return "Welcome to First Service";
}
@GetMapping("/check")
public String check(HttpServletRequest request){
log.info("Server port={}", request.getServerPort());
return String.format("Hi, there. This is a message from First Service on PORT %s", env.getProperty("local.server.port"));
}
}
HttpServletRequest 의 getServerPort() 를 이용하거나 Environment.getProperty()를 이용하면 된다.
브라우저에 http://127.0.0.1:8000/first-service/check 를 입력해보니 라운드로빈 방식으로 게이트웨이가 로드 밸런싱을 하고 있음을 확인 할 수 있다.